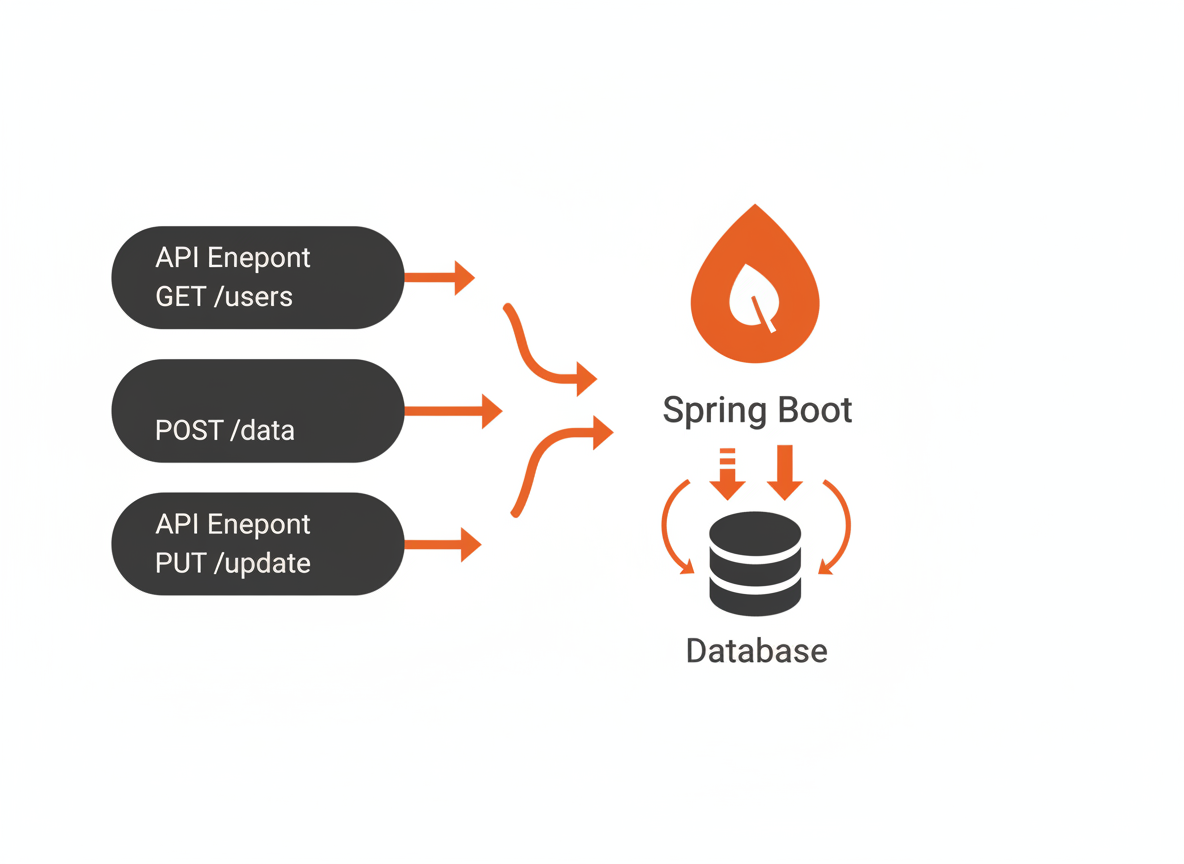
You’ve learned Spring Boot basics. Now it’s time to build something real. This project creates a complete REST API for managing a book collection. It covers all the patterns you’ll use in production: layered architecture, database persistence, validation, error handling, and testing.
By the end, you’ll have an API that handles CRUD operations, validates input, returns proper HTTP status codes, and persists data to a database.
What We’re Building
A Book Management API with these endpoints:
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/books | List all books |
| GET | /api/books/{id} | Get a single book |
| POST | /api/books | Create a new book |
| PUT | /api/books/{id} | Update an existing book |
| DELETE | /api/books/{id} | Delete a book |
| GET | /api/books/search?author=X | Search by author |
Project Setup
Go to start.spring.io and create a new project:
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.2.x
- Group: com.example
- Artifact: bookapi
- Packaging: Jar
- Java: 21
Add these dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- H2 Database
- Validation
Download, extract, and open in your IDE.
Project Structure
We’ll organize code by layer:
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi/
BookapiApplication.java
model/
Book.java
repository/
BookRepository.java
service/
BookService.java
controller/
BookController.java
exception/
BookNotFoundException.java
GlobalExceptionHandler.java
dto/
BookRequest.java
BookResponse.javaStep 1: The Entity
Create the Book entity that maps to a database table:
package com.example.bookapi.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
@Entity
@Table(name = "books")
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String author;
private String isbn;
@Column(name = "published_date")
private LocalDate publishedDate;
private String genre;
@Column(length = 2000)
private String description;
// Default constructor required by JPA
public Book() {}
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
// Getters and setters
public Long getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; }
public String getTitle() { return title; }
public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; }
public String getAuthor() { return author; }
public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; }
public String getIsbn() { return isbn; }
public void setIsbn(String isbn) { this.isbn = isbn; }
public LocalDate getPublishedDate() { return publishedDate; }
public void setPublishedDate(LocalDate publishedDate) { this.publishedDate = publishedDate; }
public String getGenre() { return genre; }
public void setGenre(String genre) { this.genre = genre; }
public String getDescription() { return description; }
public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; }
}Step 2: The Repository
Spring Data JPA generates the implementation from an interface:
package com.example.bookapi.repository;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Long> {
// Spring generates these queries from method names
List<Book> findByAuthorContainingIgnoreCase(String author);
List<Book> findByGenreIgnoreCase(String genre);
List<Book> findByTitleContainingIgnoreCase(String title);
boolean existsByIsbn(String isbn);
}JpaRepository provides findAll(), findById(), save(), deleteById(), and more. The custom methods are derived from their names automatically.
Step 3: DTOs for Request/Response
DTOs (Data Transfer Objects) separate your API contract from your internal model:
package com.example.bookapi.dto;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class BookRequest {
@NotBlank(message = "Title is required")
@Size(max = 200, message = "Title must be less than 200 characters")
private String title;
@NotBlank(message = "Author is required")
@Size(max = 100, message = "Author must be less than 100 characters")
private String author;
private String isbn;
private LocalDate publishedDate;
private String genre;
@Size(max = 2000, message = "Description must be less than 2000 characters")
private String description;
// Getters and setters
public String getTitle() { return title; }
public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; }
public String getAuthor() { return author; }
public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; }
public String getIsbn() { return isbn; }
public void setIsbn(String isbn) { this.isbn = isbn; }
public LocalDate getPublishedDate() { return publishedDate; }
public void setPublishedDate(LocalDate publishedDate) { this.publishedDate = publishedDate; }
public String getGenre() { return genre; }
public void setGenre(String genre) { this.genre = genre; }
public String getDescription() { return description; }
public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; }
}package com.example.bookapi.dto;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class BookResponse {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;
private String isbn;
private LocalDate publishedDate;
private String genre;
private String description;
public BookResponse(Book book) {
this.id = book.getId();
this.title = book.getTitle();
this.author = book.getAuthor();
this.isbn = book.getIsbn();
this.publishedDate = book.getPublishedDate();
this.genre = book.getGenre();
this.description = book.getDescription();
}
// Getters
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getTitle() { return title; }
public String getAuthor() { return author; }
public String getIsbn() { return isbn; }
public LocalDate getPublishedDate() { return publishedDate; }
public String getGenre() { return genre; }
public String getDescription() { return description; }
}Step 4: Custom Exception
package com.example.bookapi.exception;
public class BookNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public BookNotFoundException(Long id) {
super("Book not found with id: " + id);
}
}Step 5: The Service Layer
The service contains business logic and coordinates between controller and repository:
package com.example.bookapi.service;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookRequest;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookResponse;
import com.example.bookapi.exception.BookNotFoundException;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import com.example.bookapi.repository.BookRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
@Transactional
public class BookService {
private final BookRepository bookRepository;
public BookService(BookRepository bookRepository) {
this.bookRepository = bookRepository;
}
public List<BookResponse> getAllBooks() {
return bookRepository.findAll().stream()
.map(BookResponse::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public BookResponse getBookById(Long id) {
Book book = bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new BookNotFoundException(id));
return new BookResponse(book);
}
public BookResponse createBook(BookRequest request) {
Book book = new Book();
mapRequestToBook(request, book);
Book saved = bookRepository.save(book);
return new BookResponse(saved);
}
public BookResponse updateBook(Long id, BookRequest request) {
Book book = bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new BookNotFoundException(id));
mapRequestToBook(request, book);
Book updated = bookRepository.save(book);
return new BookResponse(updated);
}
public void deleteBook(Long id) {
if (!bookRepository.existsById(id)) {
throw new BookNotFoundException(id);
}
bookRepository.deleteById(id);
}
public List<BookResponse> searchByAuthor(String author) {
return bookRepository.findByAuthorContainingIgnoreCase(author).stream()
.map(BookResponse::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public List<BookResponse> searchByGenre(String genre) {
return bookRepository.findByGenreIgnoreCase(genre).stream()
.map(BookResponse::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private void mapRequestToBook(BookRequest request, Book book) {
book.setTitle(request.getTitle());
book.setAuthor(request.getAuthor());
book.setIsbn(request.getIsbn());
book.setPublishedDate(request.getPublishedDate());
book.setGenre(request.getGenre());
book.setDescription(request.getDescription());
}
}Step 6: The Controller
The controller handles HTTP requests and delegates to the service:
package com.example.bookapi.controller;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookRequest;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookResponse;
import com.example.bookapi.service.BookService;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/books")
public class BookController {
private final BookService bookService;
public BookController(BookService bookService) {
this.bookService = bookService;
}
@GetMapping
public List<BookResponse> getAllBooks() {
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public BookResponse getBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
return bookService.getBookById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<BookResponse> createBook(@Valid @RequestBody BookRequest request) {
BookResponse created = bookService.createBook(request);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(created);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public BookResponse updateBook(@PathVariable Long id, @Valid @RequestBody BookRequest request) {
return bookService.updateBook(id, request);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
bookService.deleteBook(id);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<BookResponse> searchBooks(
@RequestParam(required = false) String author,
@RequestParam(required = false) String genre) {
if (author != null && !author.isBlank()) {
return bookService.searchByAuthor(author);
}
if (genre != null && !genre.isBlank()) {
return bookService.searchByGenre(genre);
}
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
}The @Valid annotation triggers validation on BookRequest. Invalid requests get rejected before reaching the service.
Step 7: Global Exception Handler
Handle exceptions consistently across all endpoints:
package com.example.bookapi.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(BookNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleBookNotFound(BookNotFoundException ex) {
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse(
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(),
ex.getMessage(),
LocalDateTime.now()
);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(error);
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> handleValidationErrors(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
Map<String, String> fieldErrors = new HashMap<>();
for (FieldError error : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
fieldErrors.put(error.getField(), error.getDefaultMessage());
}
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("status", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
response.put("errors", fieldErrors);
response.put("timestamp", LocalDateTime.now());
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleGenericException(Exception ex) {
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse(
HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(),
"An unexpected error occurred",
LocalDateTime.now()
);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).body(error);
}
// Inner class for error responses
public static class ErrorResponse {
private int status;
private String message;
private LocalDateTime timestamp;
public ErrorResponse(int status, String message, LocalDateTime timestamp) {
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
public int getStatus() { return status; }
public String getMessage() { return message; }
public LocalDateTime getTimestamp() { return timestamp; }
}
}Step 8: Configuration
Configure the database in application.properties:
# H2 Database (in-memory for development)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:bookdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
# JPA/Hibernate
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
# H2 Console (access at /h2-console)
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
# Server port
server.port=8080Step 9: Sample Data (Optional)
Add sample data on startup for testing:
package com.example.bookapi;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import com.example.bookapi.repository.BookRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.time.LocalDate;
@Configuration
public class DataLoader {
@Bean
CommandLineRunner initDatabase(BookRepository repository) {
return args -> {
Book book1 = new Book("The Pragmatic Programmer", "David Thomas");
book1.setIsbn("978-0135957059");
book1.setGenre("Technology");
book1.setPublishedDate(LocalDate.of(2019, 9, 13));
book1.setDescription("A guide to software craftsmanship.");
repository.save(book1);
Book book2 = new Book("Clean Code", "Robert C. Martin");
book2.setIsbn("978-0132350884");
book2.setGenre("Technology");
book2.setPublishedDate(LocalDate.of(2008, 8, 1));
book2.setDescription("A handbook of agile software craftsmanship.");
repository.save(book2);
Book book3 = new Book("1984", "George Orwell");
book3.setIsbn("978-0451524935");
book3.setGenre("Fiction");
book3.setPublishedDate(LocalDate.of(1949, 6, 8));
book3.setDescription("A dystopian social science fiction novel.");
repository.save(book3);
System.out.println("Sample data loaded: " + repository.count() + " books");
};
}
}Testing the API
Run the application and test with curl or Postman.
Get All Books
curl http://localhost:8080/api/booksResponse:
[
{
"id": 1,
"title": "The Pragmatic Programmer",
"author": "David Thomas",
"isbn": "978-0135957059",
"publishedDate": "2019-09-13",
"genre": "Technology",
"description": "A guide to software craftsmanship."
},
...
]Get Single Book
curl http://localhost:8080/api/books/1Create a Book
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/books \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"title": "Effective Java",
"author": "Joshua Bloch",
"isbn": "978-0134685991",
"genre": "Technology",
"publishedDate": "2018-01-06"
}'Response (201 Created):
{
"id": 4,
"title": "Effective Java",
"author": "Joshua Bloch",
...
}Update a Book
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/api/books/4 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"title": "Effective Java, 3rd Edition",
"author": "Joshua Bloch",
"isbn": "978-0134685991",
"genre": "Technology"
}'Delete a Book
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8080/api/books/4Response: 204 No Content
Search by Author
curl "http://localhost:8080/api/books/search?author=martin"Validation Error
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/books \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"title": "", "author": ""}'Response (400 Bad Request):
{
"status": 400,
"errors": {
"title": "Title is required",
"author": "Author is required"
},
"timestamp": "2026-01-02T14:30:00"
}Not Found Error
curl http://localhost:8080/api/books/999Response (404 Not Found):
{
"status": 404,
"message": "Book not found with id: 999",
"timestamp": "2026-01-02T14:30:00"
}What You Built
This project demonstrates patterns used in production APIs:
Layered architecture: Controller, Service, Repository separation. Each layer has clear responsibilities.
DTOs: Separate request/response objects from internal entities. Change your database model without breaking the API.
Validation: Input validation with meaningful error messages before data reaches your business logic.
Exception handling: Consistent error responses across all endpoints. Clients know what to expect.
Dependency injection: Spring wires components together. Easy to test and swap implementations.
Next Steps
Extend the project with these features:
Pagination: Return books in pages instead of all at once. Use Spring Data’s Pageable.
Authentication: Add Spring Security to protect endpoints. JWT tokens for stateless auth.
PostgreSQL: Replace H2 with a real database for production use.
Docker: Containerize the application for deployment.
OpenAPI/Swagger: Generate API documentation automatically.
Unit tests: Test service logic with mocked repositories.
Integration tests: Test the full request/response cycle.
Prerequisites: Introduction to Spring Boot | Introduction to JDBC | Introduction to Maven
Related: Build a To-Do List App | Java Collections Framework | Java Exception Handling